Ultimate for Holistic Health.
<Visit ourYoga

This in itself is an Asana of Yoga, a variation of Yoga.
Our Services
Asthma, Spinal disorder, Digestive disorder Lack of sexual potentiality Weak glands and nervous system
Obesity
This is a condition in which there is an excessive amount of body fat accumulate in fat depots.
The Body Mass Index (BMI) is used to define nutritional status. It is derived from the formula i.e., (Weight in kilograms) divided by (Height in Meter)2
BMI Relative Risk
20 - 25 Less
30 - 35 Medium
35 - 40 More
40 Maximum
So, normal range is 20 -25, obesity is taken to start at 30, gross obesity at 40.
This standards are the same for men and women.
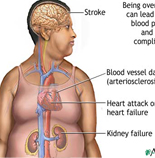
Causes:-
(a)Most prevalent in middle-age, but can occur at any stage of life.
(b)Common among the rich in our country due to consume lots of proteins, fat and carbohydrate in their diet.
(c)Hereditory factor may be positive in some cases.
(d)Endocrinal:-
(i)Hypothyroidism
(ii)Cushing's syndrome
(iii)Hypopituitarism
(iv)Pregnancy
(v)Menopause
(e)Emotional instability causes overeating as a habit.
(f)Sedentary habit persons.
Clinical features:-
(a) Body weight progressively increases.
(b) The contour and configuration of the body is altered.
(c) Buffalo type of fat distribution in Cushing's syndrome in head,neck,trunk,shoulder and spare of legs.
(d) Local fat swelling may be painful called adiposis dolorosa.
(e) Slow movements.
(f) Slightest exertion may give rise to dyspnoea.
(g) Due to high position of the diaphragm few symptoms are observed i.e., Somnolence, Hypoxia, Hypercapnia, Cyanosis,, Hypertension, Right Ventricular Hypertrophy.
(h) May be menstrual disturbances in females.
(i) Emotional upsets.
Treatment:-
After proper case-taking and investigating the hormone assay and examining the fat content of the patient and excluding the main cause of this disease the treatment starts.
Homoeopathic medicines:-
Here I am giving the name of some homoeopathic medicines which are usually prescribed in the case of this disease according to the physical signs and symptoms as usually observed in the case of this disease. However it must be borne in our mind that apart from the physical symptoms there are also some mental symptoms associated with this disease for which I have not mentioned any medicine here. Here medicines are not found in large numbers. Few medicines which act on the fatty deposits and at the same time cover the total patient. Here a few medicines are given which are more effective such as:-
(iii)Graphites
(iv)Kali bromatum
(v)Phytolacca
(vi)Thyroidinum, etc.
Except the above medicines many other medicines are used which are also essential for curing this disease.
Yogapathic treatment:-
Walking and jogging in morning and in evening is very useful.Swimming is also very effective. Few free hand exercises are also essential.
Many asanas are effective for this disease. Amongst them following are more effective such as:-
(i)Yogamudra
(ii)Sarbangasana
(iii)Padahastasana
(iv)Ardhachandrasana
(v)Utthitapadasana, etc.
Meditation:-
After lunch and dinner meditate by sitting on Vajrasana for 30 minutes.
Diet chart:-

Whatever may be the ultimate cause of obesity in the individual case the immediate cause is energy imbalance and therefore, weight reduction can be achieved only by reducing energy intake.
Long term results are best achieved where patients are well motivated and educated, follow structured diets designed to provide 800 to 1600 KCl daily and are being seen and weighed regularly, every 1-2 weeks initially, by the same person.
Diet should contain adequate protein but less fat and carbohydrate.
• Alcohol should be avoided.
• Soft drinks, cake and pastry should be avoided
• Vitamins , minerals , water and salt should not be restricted.
Here we have given a low-energy diet which is suitable for adults with obesity with or without diabetes.
• Protein 60 gms
• Carbohydrate 100 gms
• Fat 40 gms
• Energy 1000 KCal.
Early morning:-
• Protein 60 gms
• Tea - 1 Cup
• or
• Milk - 1 Cup.
Breakfast:-
• Boiled Egg - 1 piece (30 gms)
• Bread - 2 Pieces (20 gms)
Mid Morning
• Cream cracker biscuit - 1 ps
• Fruit - 1 ps. (Medium size) (apple, orange, pear, banana, grapes 100gms)
Lunch
• Clear soup
• Tomato juice
• Rice - 100 gms
• Pulses - 70 gms
• Vegetables - 125 gms
• Fish/Chicken - 2 pcs. (80 gms)
• Salad - as required
Afternoon
• Bread - 2 pcs. (20 gms)
• Tea - 1 Cup
Dinner
• Bake bread (wheat) - 2 pcs.
• Pulses - 50 gms
• Vegetables - 100 gms
• Salad - as requird
Before bed
• Milk - 1 glass (150 ml)
The above diet chart may be modified according to patient's height, weight, occupation and disease conditions.




 Benefits of Suraha
Benefits of Suraha